My Advice for Collectors Navigating the Art Market amid COVID-19 Christmas 2020
Doug Woodham
Apr 29, 2020 5:18pm
A woman walks past a fresco mural with “Atchoum! Covid 19” as the lockdown continues due to the coronavirus outbreak. Photo by Mehdi Taamallah/NurPhoto via Getty Images
Most collectors have managed through economic dislocations before. Yet the COVID-19 calamity rushing through the world economy is frightening. The collapse in business activity that started in February is far more severe than in previous recessions. Hopefully we are almost through the big pause. But the path from lockdowns to economic growth is uncertain and dependent on governments making smart policy choices, queasy consumers regaining their confidence, and businesses finding clever ways to incorporate new health protocols into their operations.
The pandemic has already hobbled the art world. Museums, galleries, and auction houses are closed and laying off staff. Art fairs slated for the spring and summer have been postponed, shifted online, or canceled entirely. Artists banking on sales from upcoming shows are wondering where their next paycheck will come from—one survey found that 95 percent of artists have already lost income because of COVID-19.
With the pandemic still developing, it’s hard to predict with any accuracy its long-term impact on the art market. However, we can at least start to assess its near-term impact on collectors and what this likely means for sales and pricing over the balance of 2020.
What’s on collectors’ minds?
Right now, most collectors have more pressing matters to worry about than buying art. They’ve pressed the pause button and will likely re-engage with the art market only when there is less uncertainty about the depth of the economic downturn and the path to recovery. This is especially true for collectors who own businesses, are senior executives at companies facing financial distress, or whose family members have been stricken with the virus.
While a guess, my sense is that at least 80 percent of buyers in the United States with the means and desire to spend $50,000 or more on a work of art are sitting on the sidelines now. This is despite all the valiant efforts of galleries and auction houses to digitally engage with their clients. For most collectors, seeing something in person—be it at an art fair, a gallery, or an auction preview—is an important and fun part of the buying experience. Without it, they are quite comfortable deferring what is an expensive and discretionary purchase.
For collectors who have continued to engage with the art market, a mismatch in price expectations has prevented deals from getting done. Buyers are looking for significant discounts on pre-virus prices, in the region of 50–60 percent. But discretionary sellers are holding firm on work they consigned before the crisis hit. Business owners and other collectors needing to generate liquidity may consider selling works from their collections at lower prices in the coming months. But their first stop is often their private banker to see if they can borrow more to fund their liquidity needs, rather than selling art and incurring sales commissions and capital gains taxes. Sellers of high-quality material remain scarce.
A lurking issue for the marketplace is that art fairs, auction houses, and galleries are likely to be among the last businesses permitted to reopen. Moreover, collectors as a group tend to tilt older. As such, even when the art world “reopens,” many collectors are likely to remain cautious about re-engaging with the physical art world until COVID-19 testing and therapeutics are available. Those who are especially risk-averse may even delay going to an art fair, Broadway show, or restaurant until a vaccine is available, which may not be for another 18 months.
What does this mean for sales of art in 2020?
Courtesy of Art Fiduciary Advisors
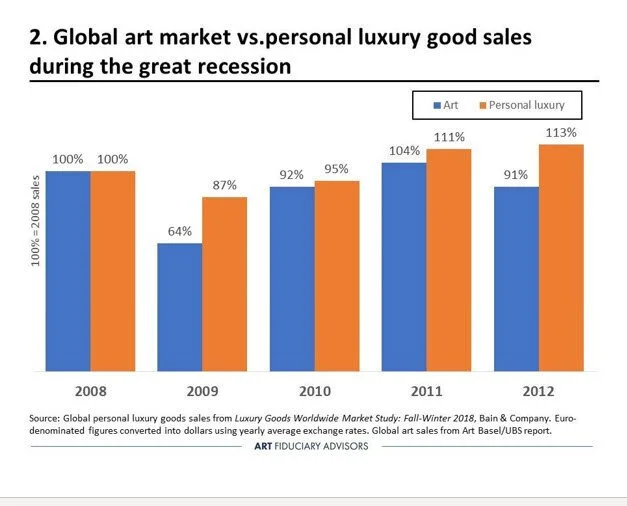
The last art market downturn started at the end of 2008, when financial panic gripped the economy. Like today, many collectors pulled back from the art market and sales plummeted. As shown above, global art market sales (as measured by the annual Art Market Report released by Art Basel and UBS) fell 36 percent in 2009. Sales struggled to recover over the next few years. The capricious nature of the art market during downturns is further illustrated in the chart below. During the last recession, the global art market declined more, and recovered much more slowly, than did global purchases of luxury handbags, jewelry, clothing, and shoes.
For 2020, my sense is that global art sales will probably decline at a sharper rate than in 2009. A decline of 50 percent, or more, is likely for three reasons. First, the current economic recession is apt to be much more severe than what happened in 2009. The unemployment rate in the United States peaked at 10 percent in October 2009. Goldman Sachs, however, recently revised its coronavirus projections, seeing a sharper downturn than originally thought. It now believes unemployment will peak at 15 percent later this year.
Courtesy of Art Fiduciary Advisors.
Second, collectors were free to wander into a gallery, attend an auction preview, or visit an art fair during the last recession. This is not possible now and will likely remain an issue for the rest of the year.
Lastly, sentiment and momentum can make a big difference in collectors’ willingness to open their wallets and purses. In February 2009, the sale of Yves Saint Laurent and Pierre Bergé’s collection provided a needed boost. Saint Laurent died of brain cancer on June 1, 2008. Later that summer, when the economy and art market were still strong, the designer’s estate announced that his fine art and decorative arts collection would be sold in Paris at Christie’s in February 2009. The sale of the 733-piece collection went ahead as planned, despite the global economic crisis that began in late 2008. The sales broke numerous records—including new auction records for Henri Matisse, Piet Mondrian, and Constantin Brancusi
—and brought in a total of $443.1 million, well above presale estimates of up to $390 million. The amazing results from these sales, which were widely reported around the world, helped remind collectors of the potential financial rewards from owning art. Yet as of April 2020, nothing like the sentiment-boosting YSL sale has been announced.
How much are sale prices likely to fall this year?
Courtesy of Art Fiduciary Advisors.
The outlook for pricing varies considerably by the artist and the quality of the work being sold. Above, I share my perspective on how much sale prices are likely to fall this year relative to what it would have cost to buy a similar work before the COVID-19 crisis.
For example, artists who regularly appear at auction tend to be the best known and most widely collected. When a masterwork becomes available for sale, either privately or at auction, collectors are often willing to “stretch” for what they may deem a once-in-a-decade opportunity. Their willingness to stretch is unlikely to be deterred by a steep recession, which is why the price they would pay this year is likely to be the same as if they bought it in 2019.
But a good work by the same artist will elicit a different response. The absence of so many buyers from the market means the seller will have to agree to a discount. Because the artist is well known, the size of the discount is bounded on the bottom by speculative buyers willing to commit capital in the hopes of flipping the work later. Artworks in this category are likely to sell for 10–25 percent less than what they would have gone for last year. As for minor works by these artists, because speculators don’t chase them, nor do seasoned collectors, sellers will have to agree to even greater discounts to get a deal done.
Artists further down the matrix tend to have fewer collectors who are aware of or interested in their work. There are also fewer, if any, speculators willing to commit capital to these types of artists now. As a result, galleries will need to entice buyers with substantial discounts, relative to the first tier of artists, if they hope to get deals done.
What financial issues should collectors be considering now?
As the COVID-19-induced lockdown continues to play out, collectors need to be mindful of four art-related financial topics:
Pricing and liquidity. Most artworks will not only decline in value this year, but the ability of collectors to convert them into cash will also be diminished significantly. Put differently, the heightened illiquidity of art means that collectors will have to wait longer, and bear higher sales commissions, when monetizing an artwork. The longer this situation persists, the more problematic it becomes for more collectors. For example, collectors who levered themselves up may soon face capital calls from their private bankers. Collectors who were thinking about tapping the value of their collections next year will need to rethink the role of art in their household balance sheet. Planners and executors will need to anticipate a much longer runway for selling artworks, in addition to lower sale proceeds being available for beneficiaries and the IRS.
Consignments. Collectors are often surprised to learn that when they consign a work to a gallery or dealer, they risk losing their rights to it if, during the consignment period, the intermediary goes bankrupt owing money to a secured creditor. During recessions, when many small businesses are especially vulnerable to bankruptcy, it’s important for consignors to put protections in place so their works cannot be seized by creditors of the gallery or dealer. Doing so will require the collector to file what are called Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) documents in the state where the gallery or dealer is domiciled. When properly filed, these documents can help prevent creditors from taking title to a consigned artwork.
Gifting. With valuations likely to be lower this year, collectors with faith in the long-term value of their art—and who have not already used their full federal estate-tax exemption—may want to consider gifting artworks.
Donating. As part of the recent CARES (Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security) Act, Congress created temporary measures to encourage cash donations to nonprofits such as art museums. Taxpayers who itemize can now deduct up to 100 percent of their adjusted gross income (AGI) for cash contributions made in 2020, instead of the usual 50–60 percent limitations. Gifts in excess of 100 percent of AGI remain eligible for the normal five-year carryforward rules.
If you have any questions about these ideas or other topics covered in this article, you can contact the author at dwoodham@artfiduciaryadvisors.com. A version of this op-ed first appeared on the author’s website.
Doug Woodham is Managing Partner of Art Fiduciary Advisors, former President of Christie’s for the Americas, and author of Art Collecting Today: Market Insights for Everyone Passionate About Art.
https://www.artsy.net/article/artsy-editorial-advice-collectors-navigating-art-market-amid-covid-19